中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (46): 7417-7421.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.46.008
• 皮肤粘膜组织构建 skin and mucosal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
异种皮覆盖薄中厚与刃厚微粒皮皮浆移植修复烧伤创面的对比
张明珠1,王建华1,历 虎1,董运凤2,齐长春1,郭宝文2,王永岭3,刘晓岩1,李云峰1,张晓慧1,刘 颖1,李兴华1,王鸿风4,郁 强4
- 1河北钢铁集团唐山钢铁有限责任公司医院烧伤科,河北省唐山市 063020;2唐山市工人医院烧伤科,河北省唐山市 063000;3解放军第二五五部队医院烧伤科,河北省唐山市 063000;4唐山市丰润区第二人民医院普外科,河北省唐山市 063000
Thin-thickness versus blade-thickness micro-skin pulping covered with heterogeneous skin for repair of burn wounds
Zhang Ming-zhu1, Wang Jian-hua1, Li Hu1, Dong Yun-feng2, Qi Chang-chun1, Guo Bao-wen2, Wang Yong-ling3, Liu Xiao-yan1, Li Yun-feng1, Zhang Xiao-hui1, Liu Ying1, Li Xing-hua1, Wang Hong-feng4, Yu Qiang4
- 1Department of Burns, Hospital of Tangshan Steel and Iron Co., Ltd., Tangshan 063020, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Burns, Tangshan Worker’s Hospital, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 3Department of Burns, Hospital of Troop 255 of Chinese PLA, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 4Department of General Surgery, the Second People’s Hospital of Fengrun Area, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
背景:采用自体微粒皮移植异体皮覆盖已成为近来修复特重度烧伤患者创面的主要手段。由于异体皮来源极为困难,因此,临床上采用异种皮(猪皮)或人工皮作为载体来覆盖创面。
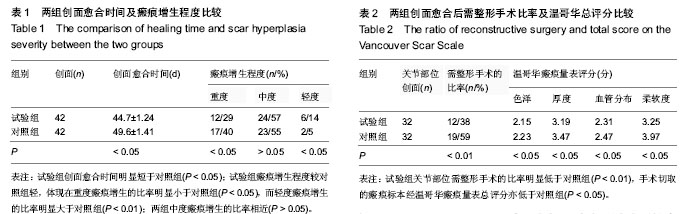
结果与结论:试验组创面平均愈合时间(44.7±1.24) d,明显短于对照组创面平均愈合时间(49.6±1.41) d (P < 0.05)。试验组移植后半年至2年创面愈合后的瘢痕增生程度轻于对照组:重度瘢痕增生的比率明显小于对照组(P < 0.05),轻度瘢痕增生的比率明显大于对照组(P < 0.01),两组中度瘢痕增生的比率相近(P > 0.05)。试验组关节部位需整复手术的比率为38%,明显低于对照组59%(P < 0.01)。试验组手术切取瘢痕的温哥华瘢痕量表总评分明显低于对照组(P < 0.05)。提示在异种皮覆盖下,通过增加微粒皮厚度,采用薄中厚微粒皮浆移植是修复大面积全层皮肤烧伤的较好方法,可获得较好的创面愈合质量。
中图分类号:
.jpg)